histamine
adaptive immune response
phagosome
MHC I
antigen
MHC II
macrophage
thymus
neutrophil
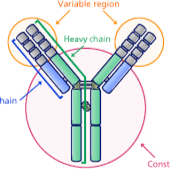
antibody
lymph
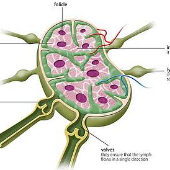
lymph node
self-antigen
pathogen
mast cell
antibiotic
bone marrow
second line of defence
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
B cell
allergic reaction
phagocyte
cell-mediated immunity
allergen
antigen-presenting cell
the name of antigen that is usually harmless but can trigger an allergic reaction
a cell capable of phagocytosis; includes macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells
an immune response directed against a specific pathogen, it retains memory of that antigen
an antigen or molecule that is a normal body component
an immune response characterised by Ig E production against a harmless antigen
a colourless fluid originating from tissue fluid
a cell that displays fragments of antigen on MHC II for presentation to T helper cells; may be macrophage, dendritic cell or B cell
a granulocyte found in tissues that releases granules containing histamine when activated
protein markers found on cell surfaces to help distinguish between self and non-self
a granular phagocyte involved in inflammation; component of pus
a membrane-bound vesicle formed around a particle during phagocytosis
a large molecule, usually protein or carbohydrate, that generates an immune response
a substance that is toxic to bacteria; may be naturally occurring or synthetically made
immune response initiated by cells, which does not involve antibodies
a chemical released by mast cells and basophils that increases blood flow and permeability of capillaries
an organ in the chest where T cells mature
a marker found on B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells
an organism foreign to the body and capable of causing disease
a class of lymphocyte that can produce antibodies
a marker found on all nucleated cells
soft tissue found in bones that produces blood cells
non-specific immune response includes inflammation and activation of complement
a large leukocyte that phagocytoses pathogens; begins as a monocyte in the blood