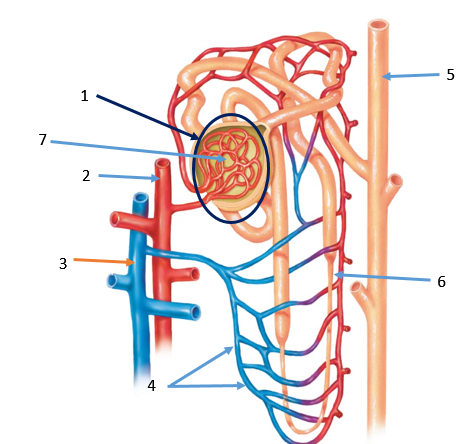
Red, white, platelets, and proteins remain in the bloodstream while water nutrients, urea, uric acid, become the filtrate
This is where the filtrate collects before going into the proximal convoluted tubule
The primary function is to collect urine in the nephron. The permeability this the membrane found here can change depending on ADH
This is where sodium is actively transported. This helps to ensure that the medulla continues to have a high salt concentration.
These structures surround the nephron. This allows the blood to reabsorb materials from the filtrate.
These structures contain filtered blood back to the heart.
These structures a filled with unfiltered blood, moving away from the heart.
This structure is where a variety materials can be absorbed back into the capillaries. Notably glucose.
This is where hydrogen ions can be secreted in order to alter the blood's pH. Bicarbonate ions be reabosrbed here to alter the pH of the blood.
This is where hydrogen ions can be secreted in order to alter the blood's pH. Bicarbonate ions be reabosrbed here to alter the pH of the blood.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) changes the permeability of the membrane in order to increase water absorption . This happens when osmotic pressure is high.
Aldosterone affects this area when blood pressure is low. Aldosterone increases the absorption of sodium, which can increase blood pressure.